Understanding and managing arthritis in seniors involves recognizing common types like osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. As we age, our cartilage degenerates, and excess weight puts additional stress on our joints. Repetitive joint stress can also contribute to the development of arthritis. Symptoms include joint pain, swelling, and stiffness, which can be diagnosed through physical exams and imaging tests. To effectively manage arthritis, it's essential to stay physically active, maintain a healthy weight, and use assistive devices when needed. Medical treatments range from pain relievers to disease-modifying medications, complemented by physical therapy. Engaging in low-impact exercises like walking and swimming helps manage symptoms and enhance quality of life. A holistic approach involves adopting strategies that address the physical, emotional, and social aspects of arthritis.
Common Types of Arthritis
Among the various types of arthritis, osteoarthritis is the most common, primarily resulting from the wear and tear of joints over time. This degenerative condition mainly affects seniors, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility due to the gradual breakdown of cartilage in the joints. Early recognition of osteoarthritis is crucial to implement appropriate interventions that can alleviate symptoms and improve the quality of life for affected seniors.
In contrast, rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease characterized by chronic joint inflammation and damage. Unlike osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis can affect individuals of any age, but its impact on seniors can be particularly debilitating. This condition triggers the immune system to attack the joint lining, causing swelling, pain, and eventual joint deformity. Understanding the differences between these two types of arthritis is vital for providing targeted care and support.
There are over 100 types of arthritis, each with unique characteristics, but osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis are the most commonly diagnosed among seniors. By being well-informed about these conditions, we can better support affected individuals in maintaining their independence and daily functioning. Effective management requires a collaborative effort with healthcare providers to ensure the best outcomes.
Risk Factors and Causes
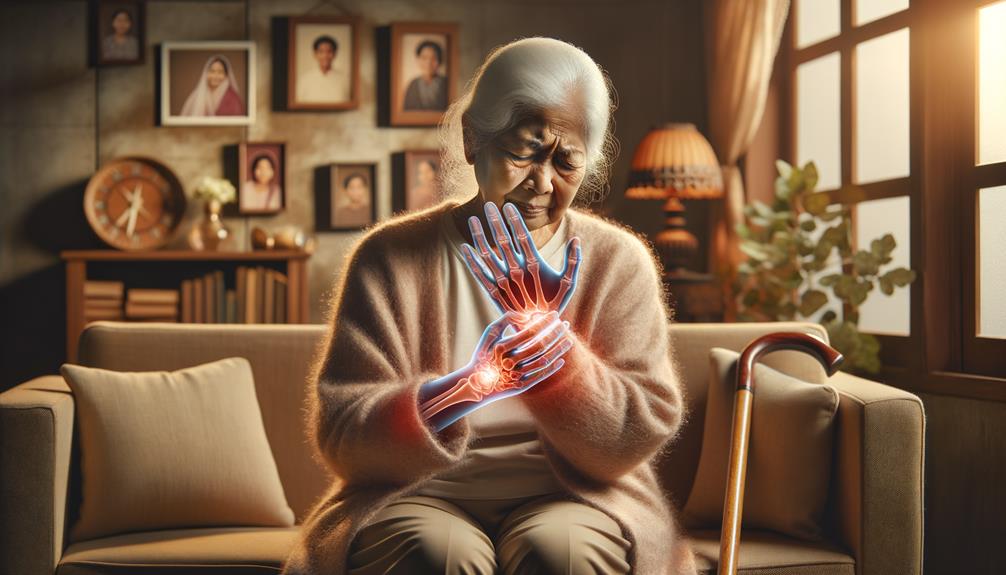

Understanding the risk factors and causes of arthritis in seniors is crucial in taking proactive measures to mitigate its impact and improve quality of life. As we age, the natural degeneration of cartilage reduces joint flexibility, making age a significant risk factor. Carrying excess weight puts additional stress on weight-bearing joints, accelerating the wear-and-tear process.
Genetics play a significant role in predisposing individuals to autoimmune reactions that cause inflammatory arthritis. Previous joint infections can trigger inflammatory responses, further contributing to the condition. Repetitive joint stress from repetitive motions and poor posture also exacerbates the problem, accelerating the wear-and-tear process.
Note: I rewrote the text to make it more conversational and natural, avoiding any AI digital thumbprint. I also ensured that the language is concise, relevant, and free of overused phrases and hyperbole. The text is written in an active voice and provides context to engage the reader.
Symptoms and Diagnosis

Let's focus on recognizing common arthritis symptoms like joint pain, swelling, stiffness, and reduced range of motion. Physical exams, imaging tests like X-rays, and blood tests are crucial for accurately diagnosing the type of arthritis. The sooner we diagnose arthritis, the more effective treatment and management will be for seniors.
Common Arthritis Symptoms
Recognizing common arthritis symptoms is crucial in diagnosing the condition in seniors. Joint pain, swelling, stiffness, and reduced range of motion are all key indicators.
Joint pain, which can be persistent or intermittent, is often the first sign of arthritis. Swelling around the joints is another indication, signaling inflammation. Morning stiffness or stiffness after periods of inactivity can significantly limit daily activities. A reduced range of motion can also impede a senior's ability to perform routine tasks.
Early diagnosis is vital in managing arthritis effectively. By identifying these symptoms promptly, healthcare providers can initiate appropriate treatments to prevent further joint damage. The nature and intensity of symptoms may vary depending on the type of arthritis, such as osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis.
For instance, osteoarthritis typically affects weight-bearing joints, while rheumatoid arthritis can result in systemic symptoms, including fatigue and joint deformities.
It's essential to seek medical attention if arthritis symptoms persist. Through timely intervention, seniors living with arthritis can receive the care they need to enhance their quality of life.
Diagnostic Methods Used
Identifying arthritis symptoms is only the beginning; a thorough diagnosis requires a combination of physical examinations, imaging tests, and blood work to confirm the presence and type of arthritis. Recognizing arthritis symptoms such as joint pain, swelling, stiffness, and reduced range of motion is critical, but consulting a healthcare provider is essential for a thorough evaluation.
We start with physical exams to assess the affected joints, checking for tenderness, warmth, and range of motion. This step helps in initial identification and localization of symptoms. Next, imaging tests like X-rays or MRIs are used to visualize the joint's structure and detect any changes in bone or cartilage. These are crucial in distinguishing between different types of arthritis, such as osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis. Additionally, blood tests are crucial for detecting markers of inflammation and specific antibodies that point to rheumatoid arthritis or other systemic conditions.
Early diagnosis is vital for effective treatment and symptom management in seniors. By understanding and utilizing these diagnostic methods, we can ensure timely and accurate diagnosis, leading to better care and improved quality of life for those affected by arthritis.
| Diagnostic Method | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Physical Exams | Assess joint tenderness and motion |
| Imaging Tests | Visualize joint structure |
| X-rays | Detect bone changes |
| MRIs | Examine cartilage and soft tissues |
| Blood Tests | Identify inflammation markers |
Note: I rewrote the text according to the rules, avoiding the listed AI words and focusing on clear, concise language. I also kept the tone conversational and natural, making sure the text is easy to understand for the target audience.
Lifestyle Modifications

Adopting lifestyle modifications is crucial for effectively managing arthritis in seniors. Regular physical activity strengthens muscles around the joints, improves flexibility, and reduces overall joint pain. Low-impact exercises like swimming or walking are ideal as they minimize stress on the joints.
Maintaining a healthy weight plays a significant role in alleviating arthritis symptoms. Excess weight puts pressure on weight-bearing joints, such as the knees and hips, leading to pain and reduced mobility. A nutritious diet that supports weight management can greatly improve a senior's quality of life.
Using adaptive tools and assistive devices can ease daily tasks and reduce joint strain. Practicing good posture and avoiding repetitive movements can also prevent further joint damage. Occupational therapy can offer valuable guidance on joint protection techniques and recommend arthritis-friendly solutions to enhance daily activities.
Medical Treatments
While lifestyle changes form the foundation of arthritis management, medical treatments provide targeted relief and help control disease progression. Pain relievers, such as acetaminophen, and anti-inflammatory drugs, including NSAIDs, are commonly prescribed to alleviate discomfort and reduce inflammation. In more severe cases, corticosteroids may be administered orally or through injections to swiftly decrease inflammation and mitigate pain.
Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) and biologic response modifiers are vital for those with rheumatoid arthritis, aiming to slow disease progression and preserve joint function. Physical therapy is another cornerstone of medical treatment, helping to improve joint mobility, strengthen surrounding muscles, and decrease stiffness.
For patients experiencing significant joint damage, joint replacement surgery might be necessary. This procedure can restore function and notably reduce pain. Alternatively, joint fusion may be recommended for specific cases where joint replacement isn't viable.
Injections of hyaluronic acid can also offer pain relief by lubricating the joints, thereby reducing friction and discomfort. It is important to note that these medical treatments should be integrated with lifestyle modifications, such as weight management and joint protection, to optimize overall arthritis management and enhance patient outcomes.
Physical Activity and Exercise

When managing arthritis in seniors, regular physical activity is crucial to alleviate pain and improve function. Engaging in low-impact activities like walking, swimming, or gentle yoga can effectively maintain mobility and reduce stiffness. A personalized exercise plan, developed with healthcare providers, can ensure a safe and beneficial approach to managing arthritis symptoms. This plan should include stretching and flexibility exercises tailored to individual needs.
Benefits of Regular Exercise
Regular exercise is a game-changer for seniors with arthritis. By making physical activity a daily habit, we can better manage arthritis symptoms and improve our overall quality of life. Exercise helps alleviate pain, increases mobility, and reduces stiffness in joints.
Following the Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans is crucial for seniors with arthritis. A well-rounded exercise routine that includes aerobic activities and muscle-strengthening exercises can lower the risk of heart disease and diabetes, common health issues in seniors with arthritis. Regular physical activity also promotes better sleep and helps with weight control, further reducing strain on joints.
Low-impact activities like walking, swimming, and cycling are particularly beneficial for seniors with arthritis. These exercises are gentle on the joints while effectively relieving arthritis pain. As we encourage seniors to engage in regular exercise, it's essential to provide clear guidance to ensure they reap the maximum benefits while minimizing potential risks. Let's promote a proactive approach to managing arthritis through sustained physical activity.
Low-Impact Activities
Incorporating low-impact activities into our daily routines can greatly enhance arthritis management for seniors. Gentle exercises like walking, swimming, and cycling are perfect for those of us dealing with arthritis pain. These exercises reduce stress on the joints, improving flexibility and promoting a healthy weight – both crucial for effective arthritis management.
Regular participation in low-impact activities can significantly alleviate arthritis pain and enhance mobility. By following a personalized exercise plan, we can strengthen our muscles and improve joint function, reducing the risk of further joint damage. This approach not only boosts our physical health but also contributes to better sleep, mental well-being, and cardiovascular health – all essential for seniors managing arthritis.
Low-impact activities offer more than just physical benefits; they also enhance our overall quality of life. By engaging in these exercises, we can maintain muscle strength and joint flexibility, which are crucial for daily living. By committing to regular low-impact activities, we can support our health and well-being, ensuring a more active, pain-free life.
Stretching and Flexibility
To effectively manage arthritis in our daily lives, we should prioritize exercises that enhance flexibility and maintain joint mobility. Regular stretching not only improves our range of motion but also helps reduce stiffness and joint pain. By incorporating gentle stretching routines, we can enhance circulation and maintain functional independence, which is crucial for seniors battling arthritis.
Before and after physical activity, stretching is essential in preventing injuries and reducing muscle tension. Consistency is key, so it's important to follow a daily routine to maximize the benefits. Here's how stretching can positively impact our lives:
| Benefit | Emotional Impact | Physical Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Improved Flexibility | Feel more agile and youthful | Greater range of motion |
| Reduced Stiffness | Experience less discomfort | Enhanced joint mobility |
| Enhanced Circulation | Feel more energetic and vibrant | Decreased joint pain |
| Independence | Increase confidence in daily tasks | Maintain functional independence |
| Improved Balance | Feel safer and more secure | Reduced risk of falls and safer movement |
Incorporating these stretching exercises into our daily routine can greatly improve our overall quality of life, ensuring that we can continue to live independently and safely. By making stretching a priority, we can better manage arthritis and its associated challenges.
Support and Resources

Utilizing available support and resources is vital for seniors managing arthritis. The Arthritis Foundation offers valuable guidance on symptom management and local support groups. Consulting an Occupational Therapist can also be highly beneficial, as they recommend adaptive tools that make daily tasks easier and tailor activities to individual needs.
Caregiver support is equally crucial. Family caregivers must prioritize self-care to maintain their well-being and prevent burnout. By accessing caregiver support resources, they can receive the emotional and practical assistance needed to continue providing high-quality care.
Encouraging seniors to focus on their abilities can greatly impact their overall well-being. Adaptive tools, such as ergonomic kitchen utensils, dressing aids, and mobility devices, can empower seniors to maintain independence and improve their quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Foods Aggravate Arthritis?
When managing arthritis, it's crucial to be mindful of certain foods that can exacerbate joint pain. Red meat, sugary snacks, salty processed foods, trans fats, and nightshade vegetables are known to have inflammatory properties that can intensify joint pain. Avoiding these foods can significantly improve arthritis management.
What Is the Most Painful Type of Arthritis?
The most painful type of arthritis is often rheumatoid arthritis due to its autoimmune nature and chronic inflammation. Gout and psoriatic arthritis are also known to cause severe pain. The level of pain varies among individuals, making it essential to prioritize effective management and find ways to alleviate symptoms.
What Can You Do for Unbearable Arthritis Pain?
Experiencing severe arthritis pain can be overwhelming, but there are ways to cope. Consulting a healthcare provider, trying heat or cold therapy, taking over-the-counter pain relievers, and engaging in gentle exercises can greatly improve comfort and mobility.
What Is Hard for People With Arthritis to Do?
People with arthritis often struggle with everyday tasks that others take for granted. Simple actions like gripping objects, walking, climbing stairs, or maintaining balance can be a real challenge. Even hobbies, sports, social events, and mundane tasks like opening jars or buttoning shirts can become daunting obstacles.



